| Chen Liang (梁宸) |
| lliangchenc@163.com |
|
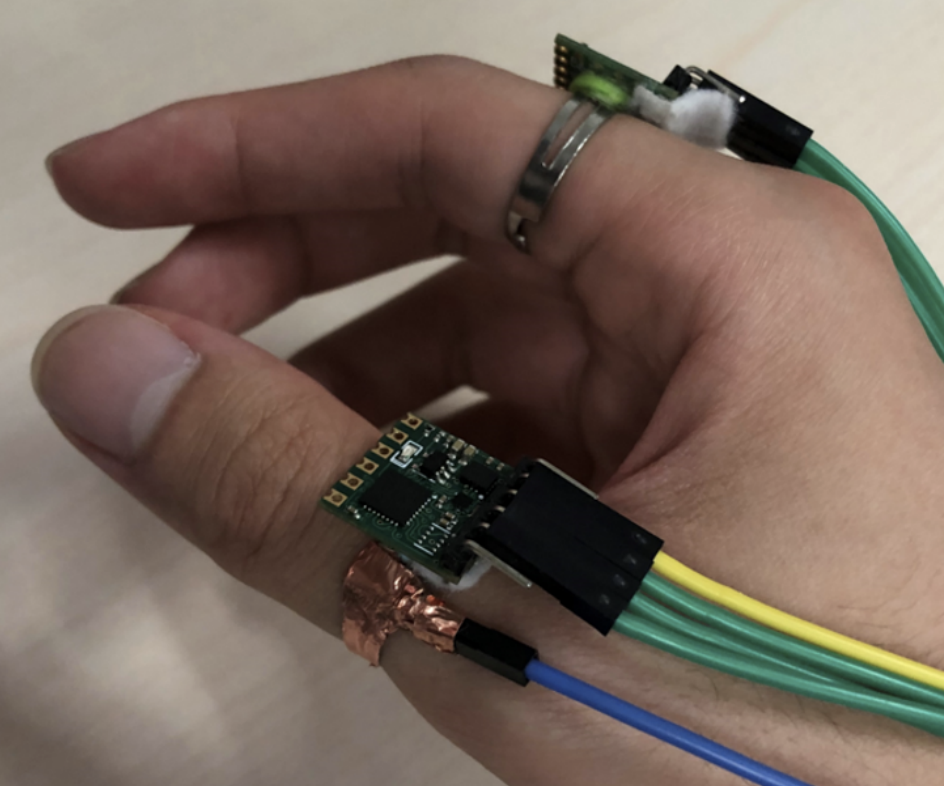
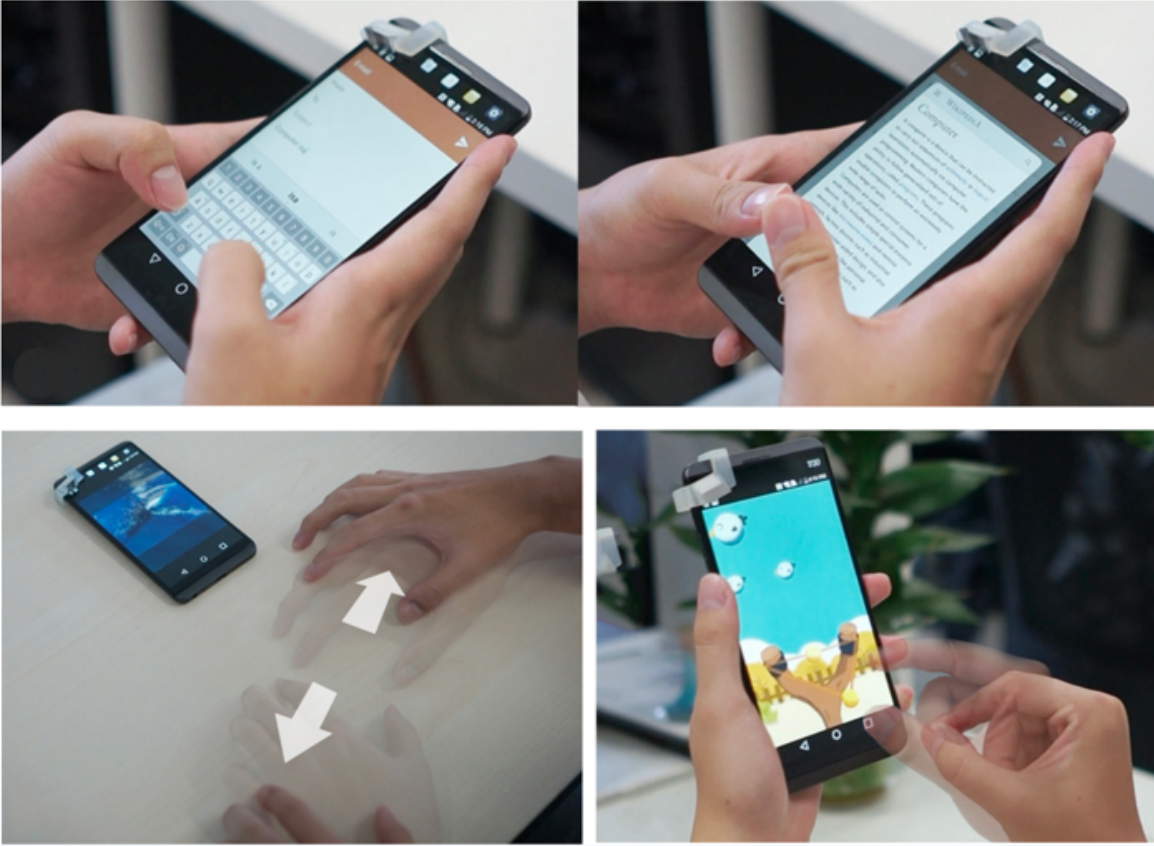
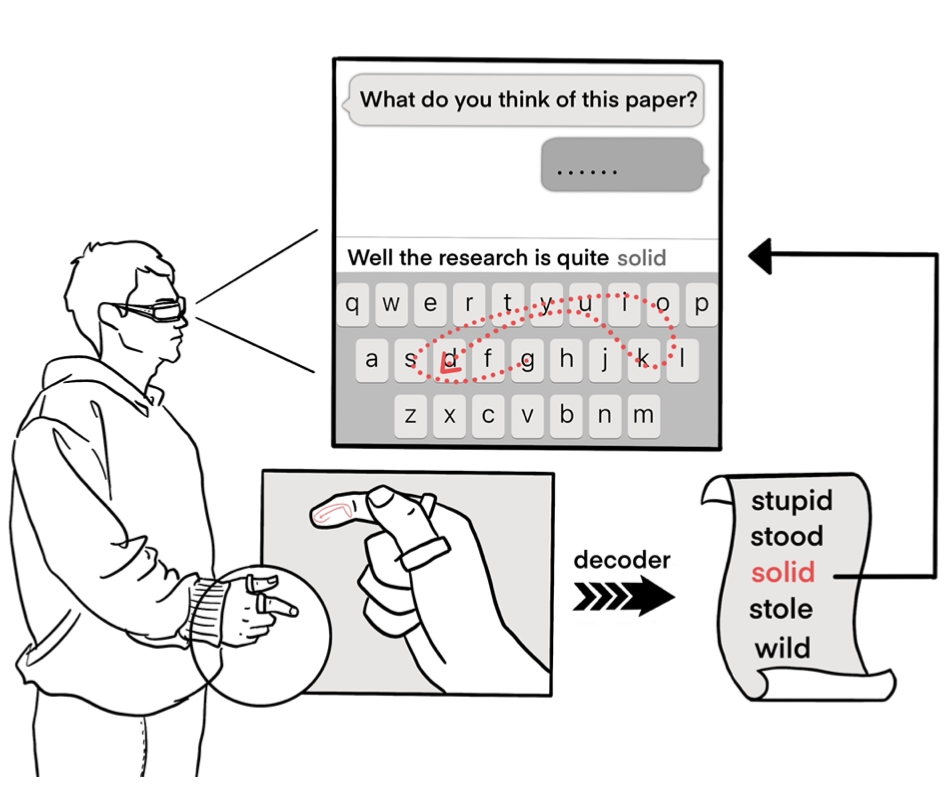
Hi! This is Chen, a third-year computer science Ph.D. candidate from Pervasive Computing Group at Tsinghua University, supervised by Prof. Yuanchun Shi and Prof. Chun Yu. I received my Bachelor's degree in Computer Science from Tsinghua University in 2019. My major research direction is Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) and I am also keeping track of research updates on natural language processing and computer vision. My research interest focuses on facilitating natural and efficient interaction schemes with compact sensor form in XR and mobile scenarios by leveraging multi-modality sensing (e.g., vision, audio, inertial signal, and RF). My previous and ongoing work expanded the user's input capability both in spatial (e.g., enabling precise input on the subtle fingertip unintrusively) and temporal (e.g., enhancing the recognition of fast and transient gestures) domains. My goal is to develop fundamental interaction techniques, with which a user can interact with everything around them seamlessly, for the next generation XR interface (just like the mouse and the keyboard for GUI). |

|